A Distinct Pattern of Myofascial Findings in Patients After Whiplash Injury
Ettlin T, Schuster C, Stoffel R, Brüderlin A, Kischka U
Reha Rheinfelden Rehabilitation Center,
Rheinfelden, Switzerland.
th.ettlin@reha-rhf.ch
OBJECTIVE: To identify objective clinical examinations for the diagnosis of whiplash syndrome, whereby we focused on trigger points. DESIGN: A cross-sectional study with 1 measurement point.
SETTING: A quiet treatment room in a rehabilitation center.
PARTICIPANTS: Patients (n=124) and healthy subjects (n=24) participated in this study. Among the patient group were patients with whiplash-associated disorders (n=47), fibromyalgia (n=21), nontraumatic chronic cervical syndrome (n=17), and endogenous depression (n=15).
INTERVENTIONS: Not applicable. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE: Each patient and control subject had a manual examination for trigger points of the semispinalis capitis, trapezius pars descendens, levator scapulae, scalenus medius, sternocleidomastoideus, and masseter muscles bilaterally.
RESULTS: Forty (85.1%) of the patients with whiplash had positive trigger points in the semispinalis capitis muscle. The patients with whiplash had a significantly higher prevalence of positive trigger points in the semispinalis capitis muscle than any of the control groups (P<.05). For the other examined muscles, the prevalence of trigger points in the patients with whiplash did not differ significantly from the patients with fibromyalgia or nontraumatic chronic cervical syndrome. It did differ from the patients with endogenous depression and the healthy controls.
CONCLUSIONS: Patients with whiplash showed a distinct pattern of trigger point distribution that differed significantly from other patient groups and healthy subjects. The semispinalis capitis muscle was more frequently affected by trigger points in patients with whiplash, whereas other neck and shoulder muscles and the masseter muscle did not differentiate between patients with whiplash and patients with nontraumatic chronic cervical syndrome or fibromyalgia.
KEY POINTS FROM DR. DAN MURPHY
- 85.1 percent of the patients with whiplash had positive trigger points in the semispinalis capitis muscle.
-
The patients with whiplash had a significantly higher prevalence of positive trigger points in the semispinalis capitis muscle than any of the control groups, which is a distinct pattern of trigger point distribution that differed significantly from other patient groups and healthy subjects.
-
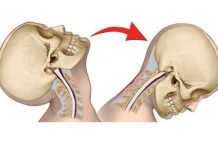
In addition to neck pain and stiffness, whiplash patients often complain about “headache, brachialgia (pain radiating into one or both arms), vertigo or dizziness, chewing and swallowing problems, visuomotor disturbances such as blurred vision and reduced coordination, fatigue and reduced energy, neuropsychologic dysfunction, depression, irritability, and sleep disorders.”
-
Whiplash pain can be caused by injuries to the muscles, facet joints, ligaments, disks, and nerve roots.
-
Reduced cervical range of motion is a prominent finding in whiplash-injured patients.
-
Myofascial tension of the scalene muscles causes a functio-nal thoracic outlet syndrome that may explain brachialgia.
-
“The only consistent finding [to explain whiplash pain] reported in the literature is a painful facet joint dysfunction C1-2,” verified by anesthetic injection.
-
These authors main hypothesis was that “patients with whiplash disorder would display more trigger points in the semispinalis capitis muscle, which is localized in the upper neck,” consistent with a C1-C2 facet injury.
-
The semispinalis capitis is an easily locatable marker for the upper cervical spine. “The semispinalis capitis was included because its referred pain zone is parieto-occipital and periorbital, which is the most frequent pattern of referred pain to the head in patients with whiplash.”
-
The criteria for myofascial pain syndrome are:
-
Palpable hardening (trigger point and/or taut band) in the muscle belly
-
Pressure pain in the trigger point or taut band
-
Referred pain while manipulating the trigger point in the taut band
-
Recognition of the elicited pain as the patient’s known and familiar pain
-
-
“The prevalence of trigger points in the semispinalis capitis muscle was significantly higher in the whiplash injury group than in each of the other groups. Patients with whiplash syndrome, therefore, showed a distinct pattern of trigger point distribution that differed significantly from other patient groups and a healthy control group.”
-
“Our findings support the hypothesis that the most severe musculoskeletal pathology after whiplash is found in the upper part of the cervical spine.” They are consistent with the biomechanics of the injury and of a “painful C1-2 facet joint dysfunction. In contrast, trigger points in the other patient groups and in healthy people were predominantly found in the lower cervical spine and the shoulder girdle.”
-
Trigger points are a neuromuscular dysfunction at the motor endplate of a skeletal muscle fiber.
-
A mechanical trauma stimulates the release of excessive amounts of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction and increased intracellular calcium activates local muscle contraction. This causes increased metabolism [use of oxygen to produce ATP] and relative local ischemia; this leads to failure of the calcium pump which is required for the muscle to relax. “Consequently, the calcium continues to stimulate contraction, and a vicious circle develops.”
-
“The semispinalis capitis muscle was more frequently affected by trigger points in patients with whiplash, whereas other neck and shoulder muscles and the masseter muscle did not differentiate between patients with whiplash and patients with nontraumatic chronic cervical syndrome or fibromyalgia.”
Dr. Dan Murphy graduated magna cum laude from Western States Chiropractic College in 1978. He received Diplomat status in Chiropractic Orthopedics in 1986. Since 1982, Dr. Murphy has served part-time as undergraduate faculty at Life Chiropractic College West, currently teaching classes to seniors in the management of spinal disorders. He has taught more than 2000 postgraduate continuing education seminars. Dr. Murphy is a contributing author to both editions of the book Motor Vehicle Collision Injuries and to the book Pediatric Chiropractic. Hundreds of detailed Article Reviews, pertinent to chiropractors and their patients, are available at Dr. Murphy’s web page, http://www.danmurphydc.com/