Tissue Plasminogen Activator in a Vertebral Artery Dissection
Andrew P. Gasecki, Carmelo Graffagnino and Vladimir Hachinski
Division of Neurology,
University of Nebraska Medical Center,
Omaha 68198-2045, USA.
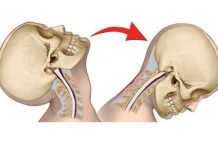
Background: Spontaneous dissection of the vertebral artery is uncommon.
Method: Case study.
Results: We report a 49-year-old woman who presented with the rapidly progressing basilar artery syndrome who was given an intravenous dose of tissue plasminogen activator seven hours after the onset of first symptoms. Thirty minutes after the injection, a dramatic recovery of the patient’s consciousness and neurological signs was noted.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator use in acute vertebral artery dissection.